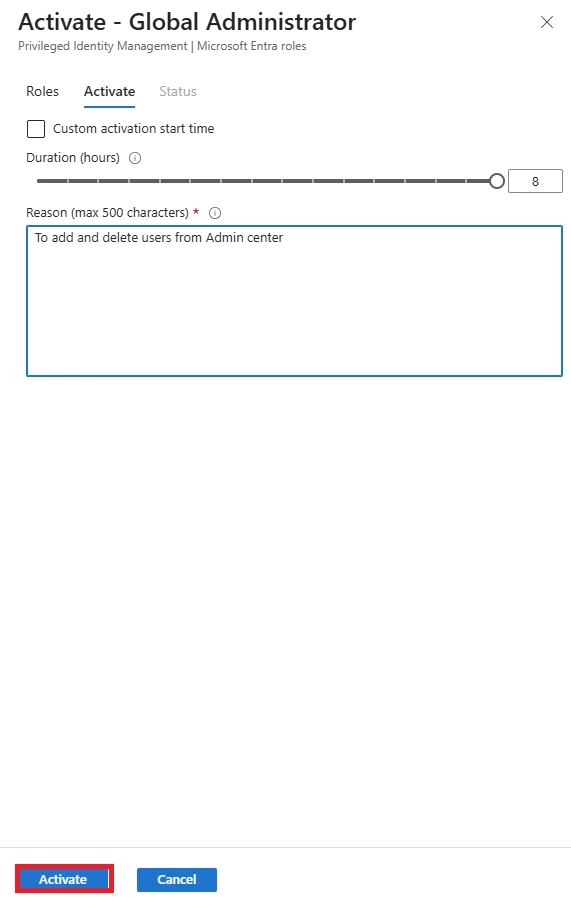
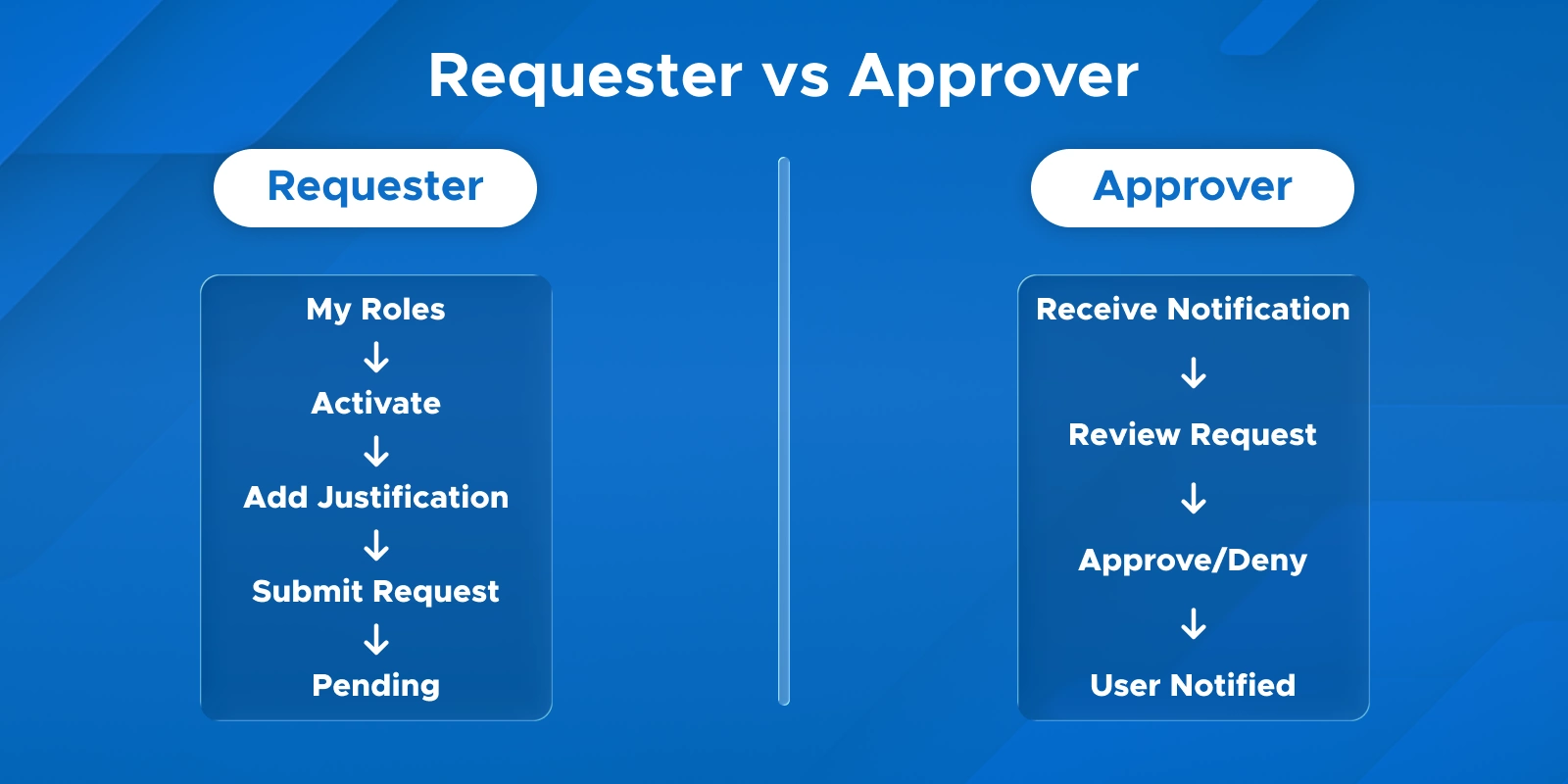
Q: What is manual vs auto approval in Microsoft PIM?
A: Manual approval in Microsoft PIM roles means an eligible role activation must be explicitly approved by another user before it takes effect. Auto approval in Privileged Identity Management means the activation is immediate with no human intervention. Manual = “Approval required PIM role activation”, auto = no approval needed.
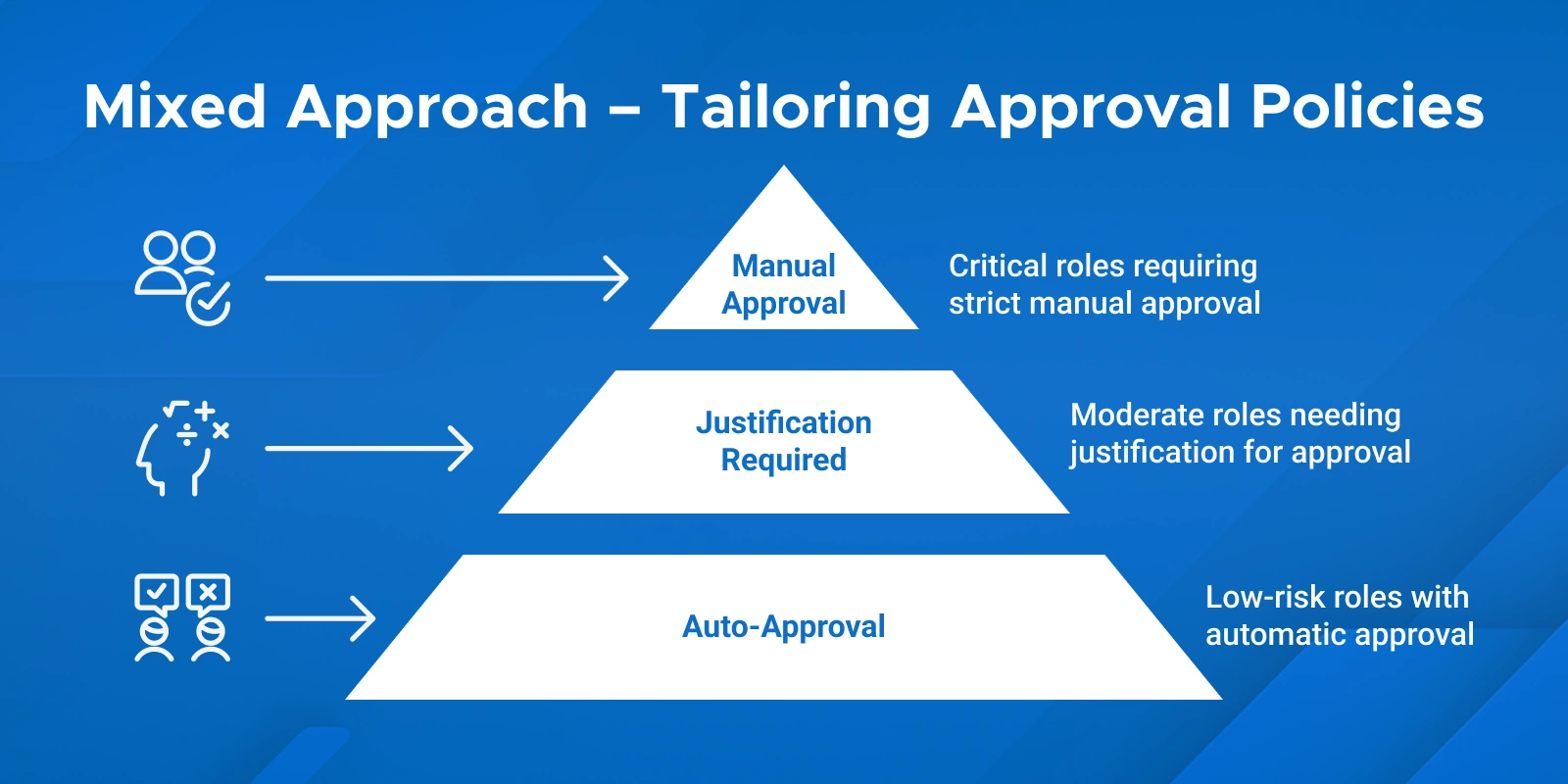
Q: How do I set auto approval for PIM roles? Can I bypass approval for certain PIM roles?
A: To enable auto-approval for low-risk PIM roles or bypass manual approval, go to PIM role settings and uncheck “Require approval to activate”. Eligible users can then activate roles automatically. This applies per role, so all users assigned to that role follow the same auto-activation rule.
Q: How to configure manual approval for PIM roles in Microsoft 365?
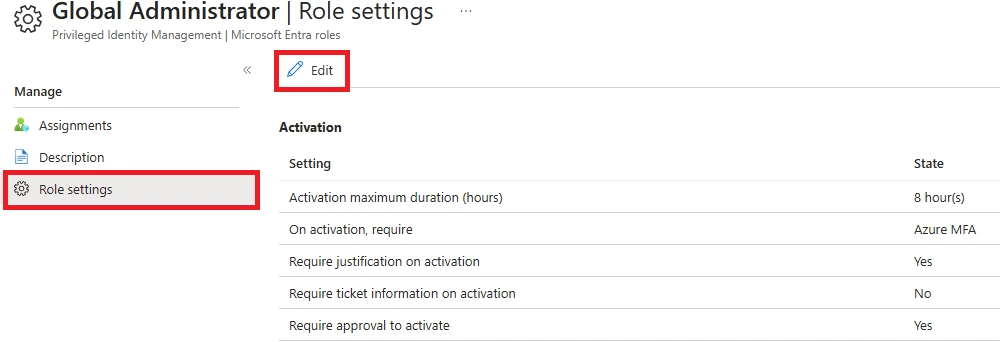
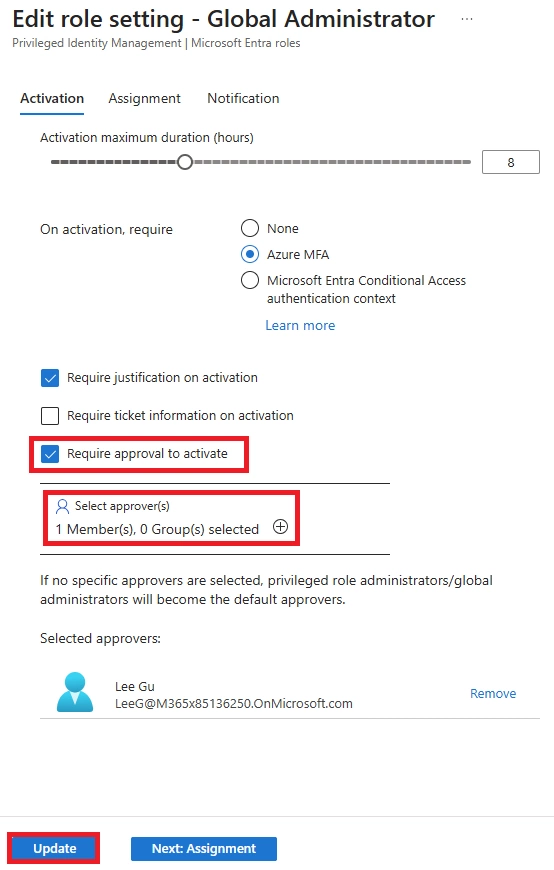
A: Navigate to the role’s PIM settings, enable “Require approval to activate”, and assign delegated approvers. This sets up the approval workflow for Azure resource roles PIM, ensuring manual oversight before activation.
Q: Which PIM roles should always require manual approval?
A: Highly privileged roles like Global Administrator, Privileged Role Administrator, Exchange Admin, SharePoint Admin, or Azure Subscription Owner should always require manual approval. Any role that can significantly alter security or compliance settings should follow the approval required vs auto-activate eligible roles PIM model.
Q: What are the risks of auto-approving PIM role activations?
A: Risks include compromised accounts activating sensitive roles without oversight, accidental role misuse, and non-compliance with security policy. These risks are part of enterprise risk assessments: auto approval trade-offs. Mitigate them with MFA, justification, short activation windows, and monitoring.
Q: How long does a PIM approval request last?
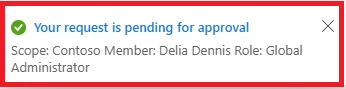
A: PIM approval requests have a role activation window and approval expiration of 24 hours. If not approved within that time, the request expires and the user must submit a new request.
Q: Can I approve my own PIM request?
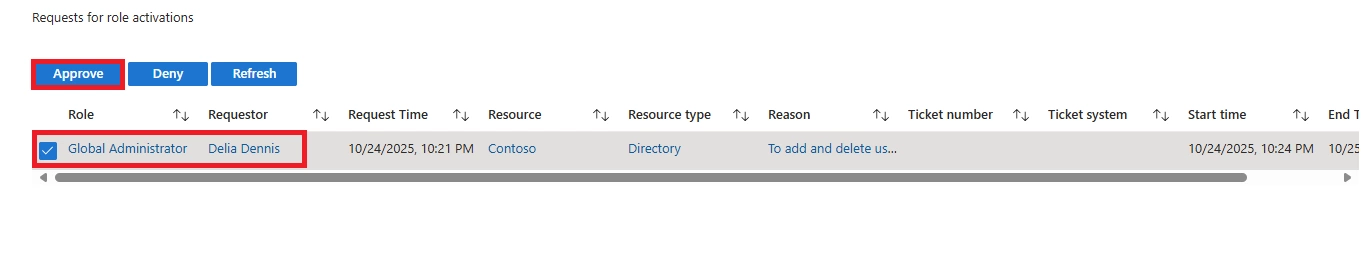
A: No. PIM enforces separation of duties. Approvers must be different users, either single or group-based, following delegated approver settings in Microsoft Entra PIM.
Q: How do you automate PIM approval using Teams Approvals?
A: PIM does not natively support Teams Approvals for automatic activation. For multi-stage or automated workflows, you must use Entra Access Packages or custom solutions.
Q: What is a PIM approval role?
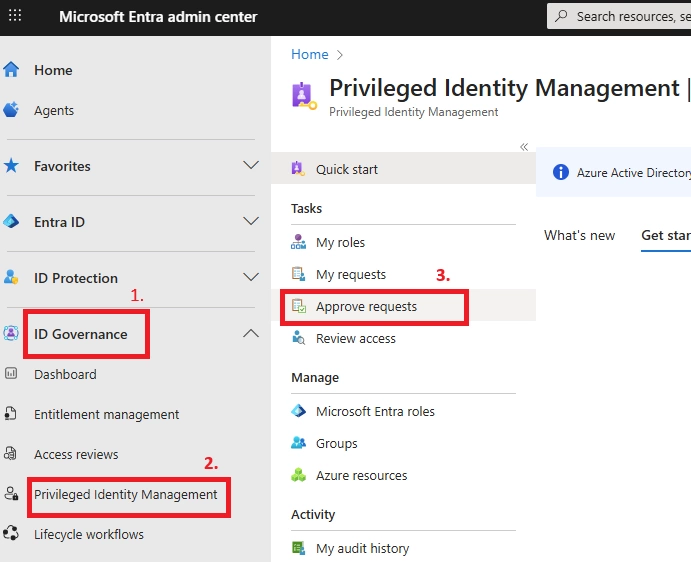
A: A PIM approval role is a designated user or group responsible for manual approval in PIM roles. They review requests before activation to enforce security and compliance.
Q: What is PIM authorization?
A: PIM authorization refers to granting eligible users the ability to activate privileged roles, either via auto approval or manual approval, within the Microsoft PIM approval workflow.
Q: An eligible user submitted a PIM request, but the approver didn’t see it – how to troubleshoot?
A: Check that the user is eligible, the role requires approval, delegated approvers are configured correctly, and notifications are working. If everything is correct but still missing, it may be a sync or permissions issue.
Q: Auto-approval not working for certain PIM roles – why?
A: Ensure “Require approval to activate” is disabled for the correct scope (Azure AD vs Azure resource roles). Tenant-wide policies or conditional access may still enforce approvals.
Q: Can I have multi-level approvals in PIM?
A: PIM allows multiple delegated approvers, but only one approval is needed. Multi-stage sequential approval requires external workflows or Entra Access Packages.
Q: How long does a PIM role stay active once approved?
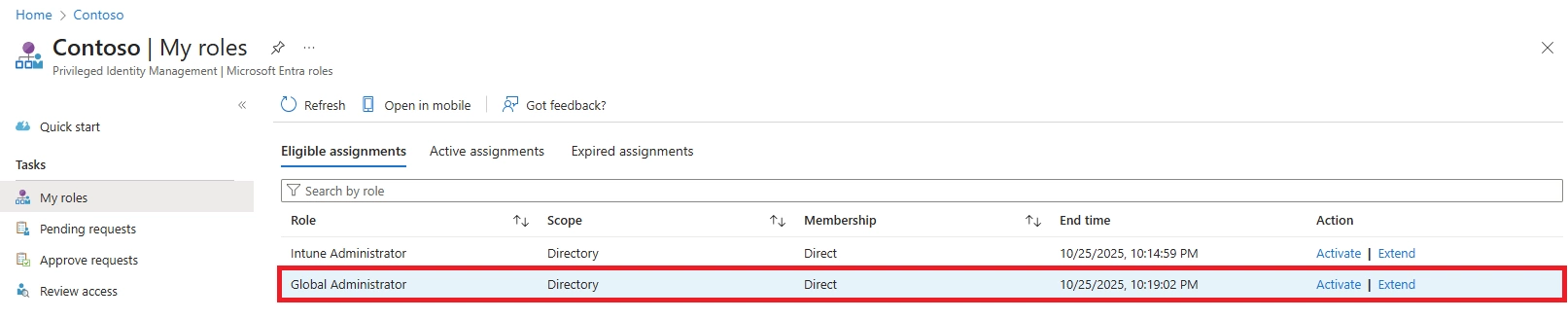
A: Roles stay active for the duration set during activation, then expire automatically. Users must request again for continued access.
Q: Do PIM approvers need to be Global Admins?
A: No. Any user can be assigned as an approver. Global Admins/Privileged Role Admins are fallback approvers if none are specified.
Q: MFA isn’t prompting during PIM activation – why?
A: Possible reasons include recent MFA session caching, “Require Azure MFA” not enabled in role settings, or Conditional Access settings bypassing repeated prompts.