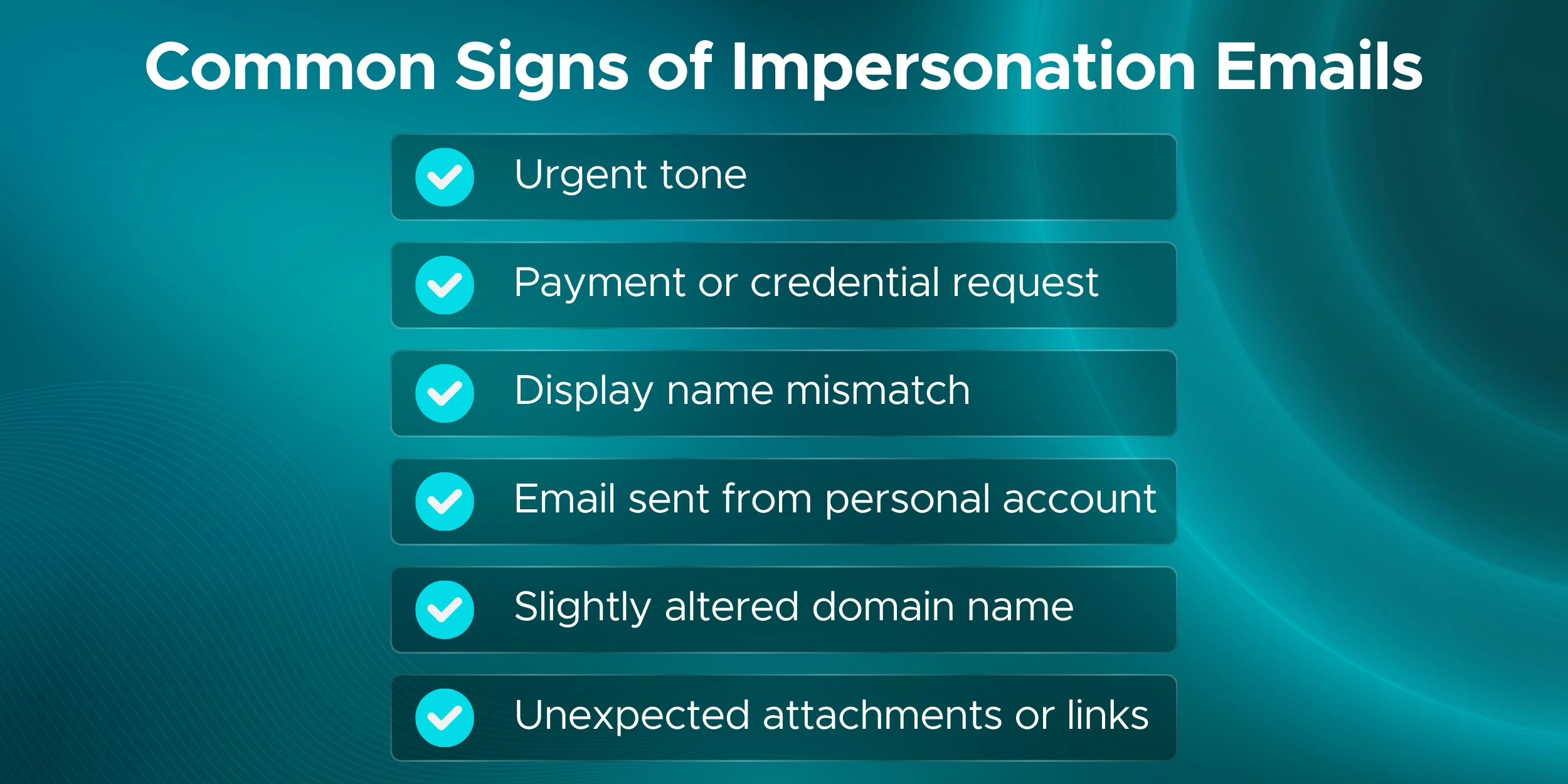
Q1. What is the anti-phishing policy in Office 365?
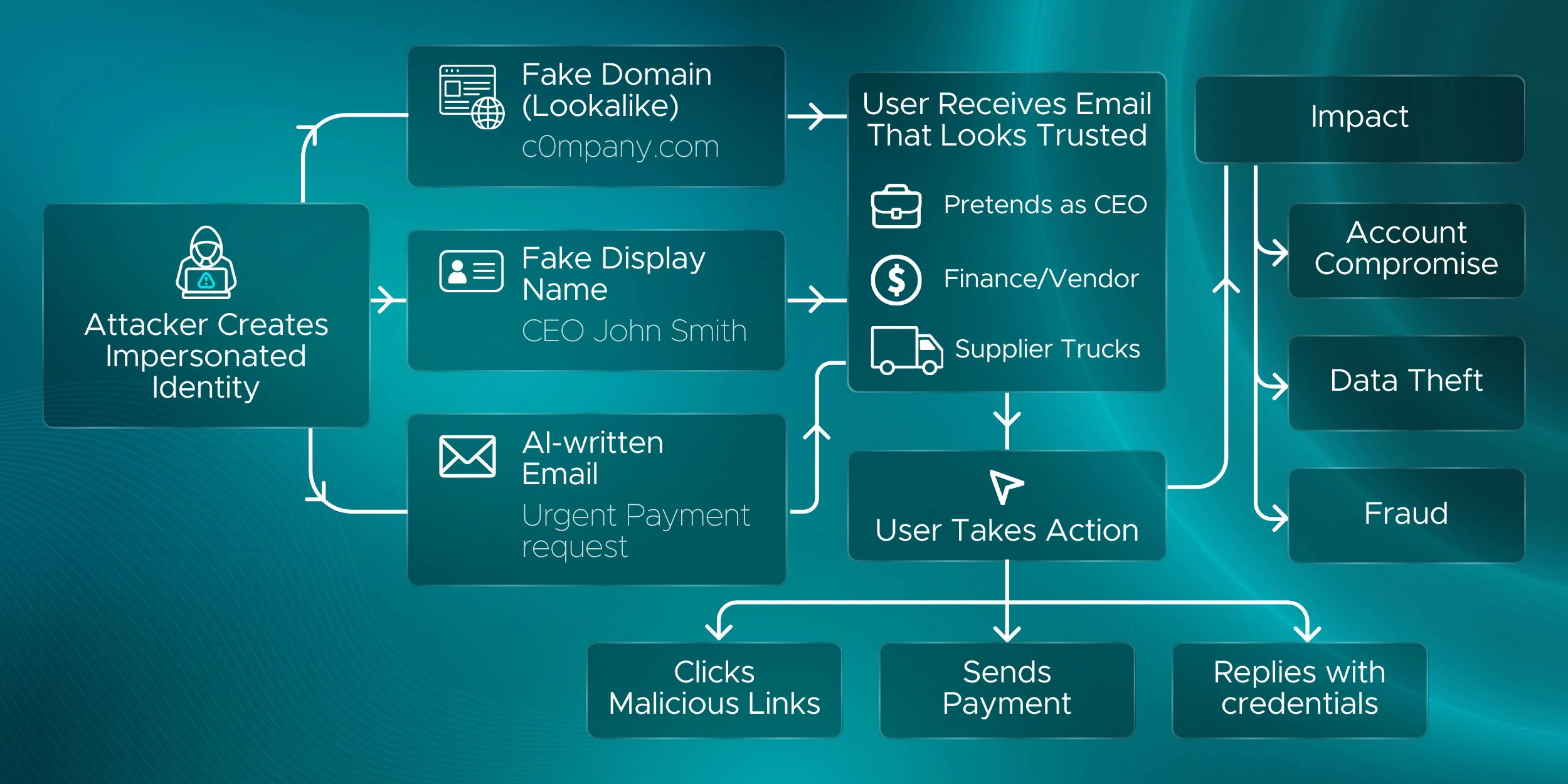
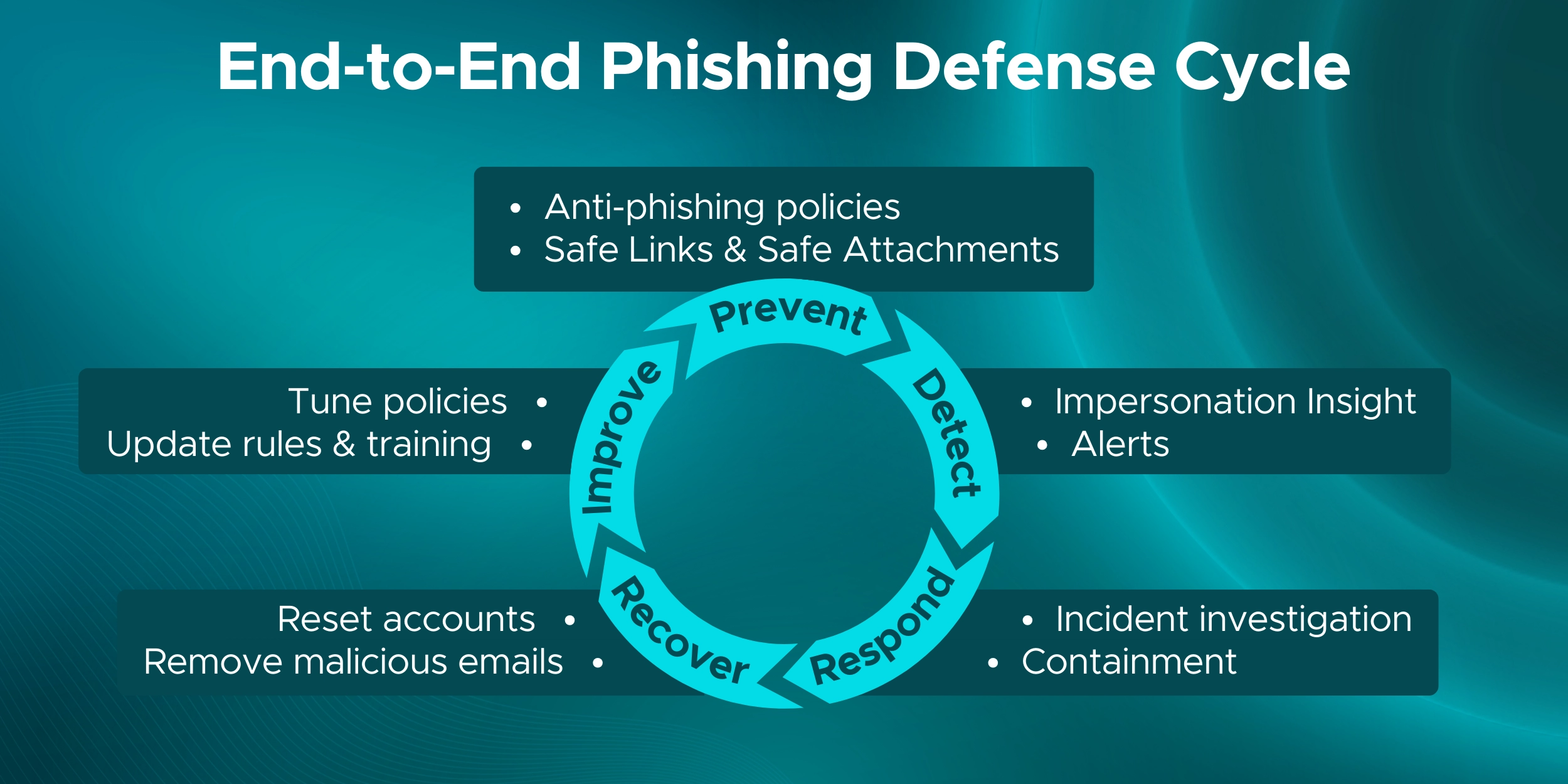
The anti-phishing policy in Office 365 is a security control that helps detect and block phishing emails, including impersonation, spoofed domains, and credential-stealing messages.
Q2. How does Microsoft 365 phishing protection work?
Microsoft 365 phishing protection uses multiple signals such as sender behavior, domain reputation, mailbox intelligence, and message content to identify and stop phishing and impersonation attacks.
Q3. How to prevent phishing emails in Office 365?
To prevent phishing emails in Office 365, configure anti-phishing policies, enable impersonation protection, turn on Safe Links and Safe Attachments, enforce SPF/DKIM/DMARC, and train users to report suspicious messages.
Q4. What is anti-phishing protection in Microsoft 365?
Anti-phishing protection in Microsoft 365 focuses on stopping emails that pretend to be trusted users, brands, or domains. It helps prevent credential theft, payment fraud, and account compromise.
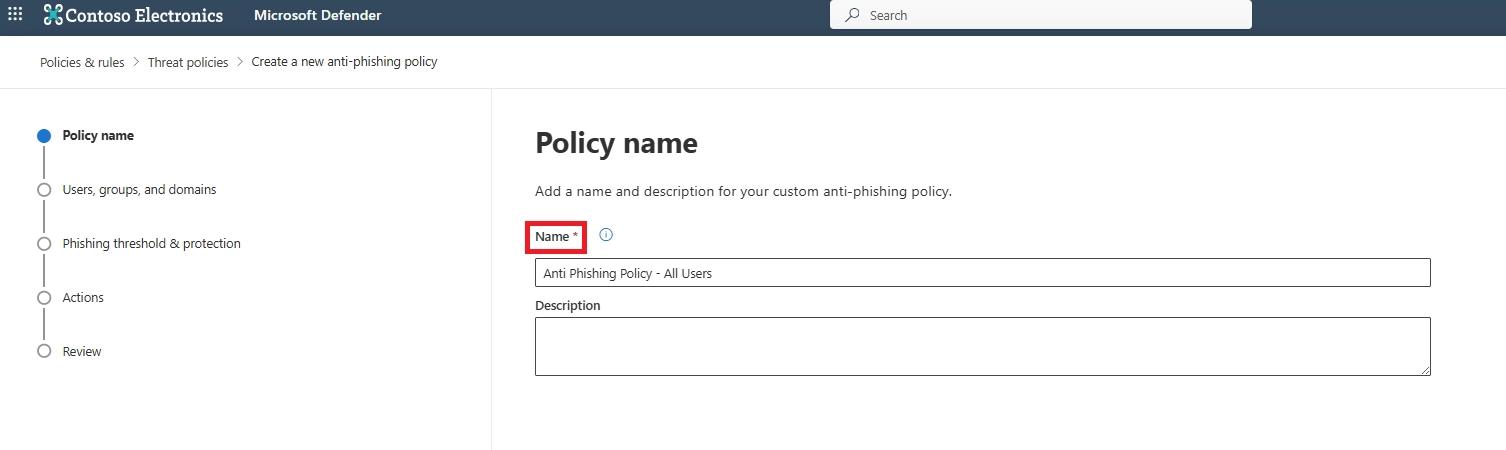
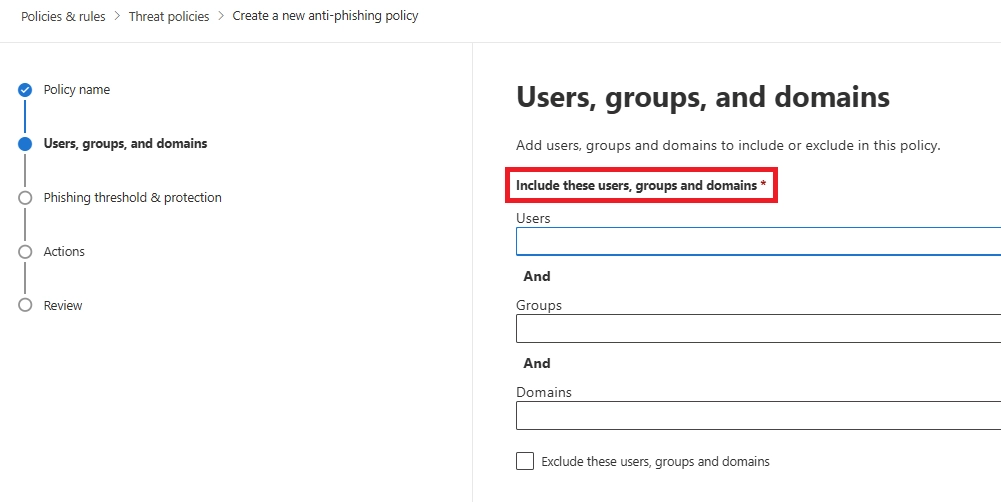
Q5. How do I set anti-phishing in Microsoft Defender?
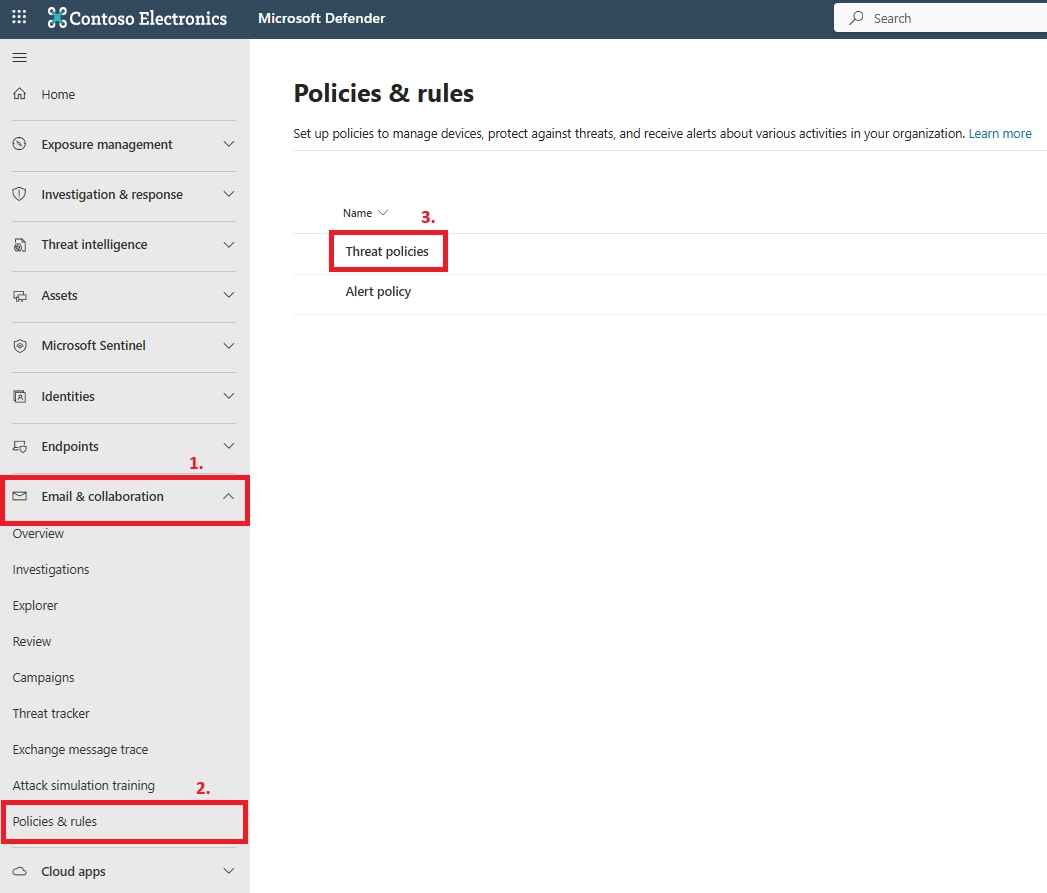
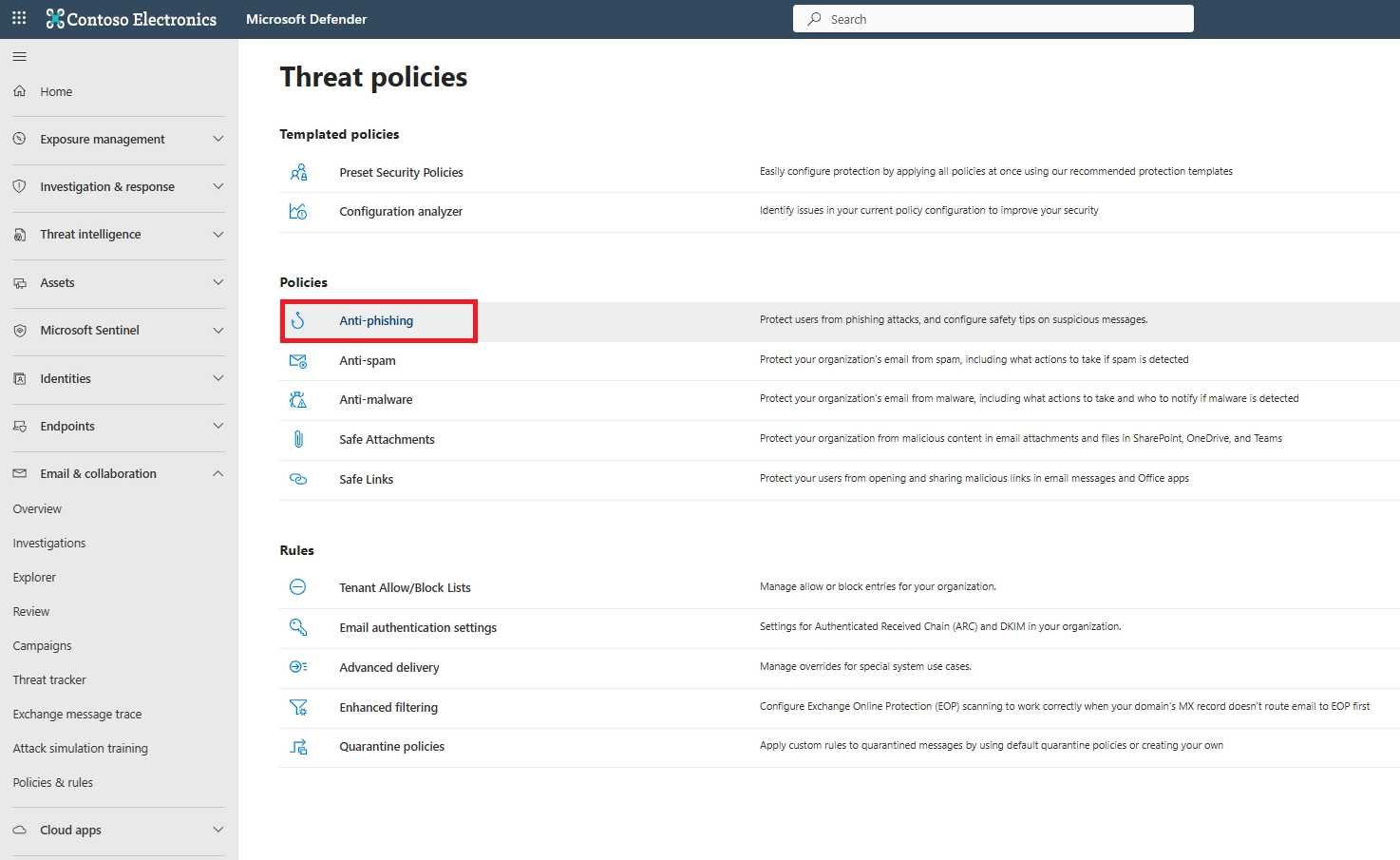
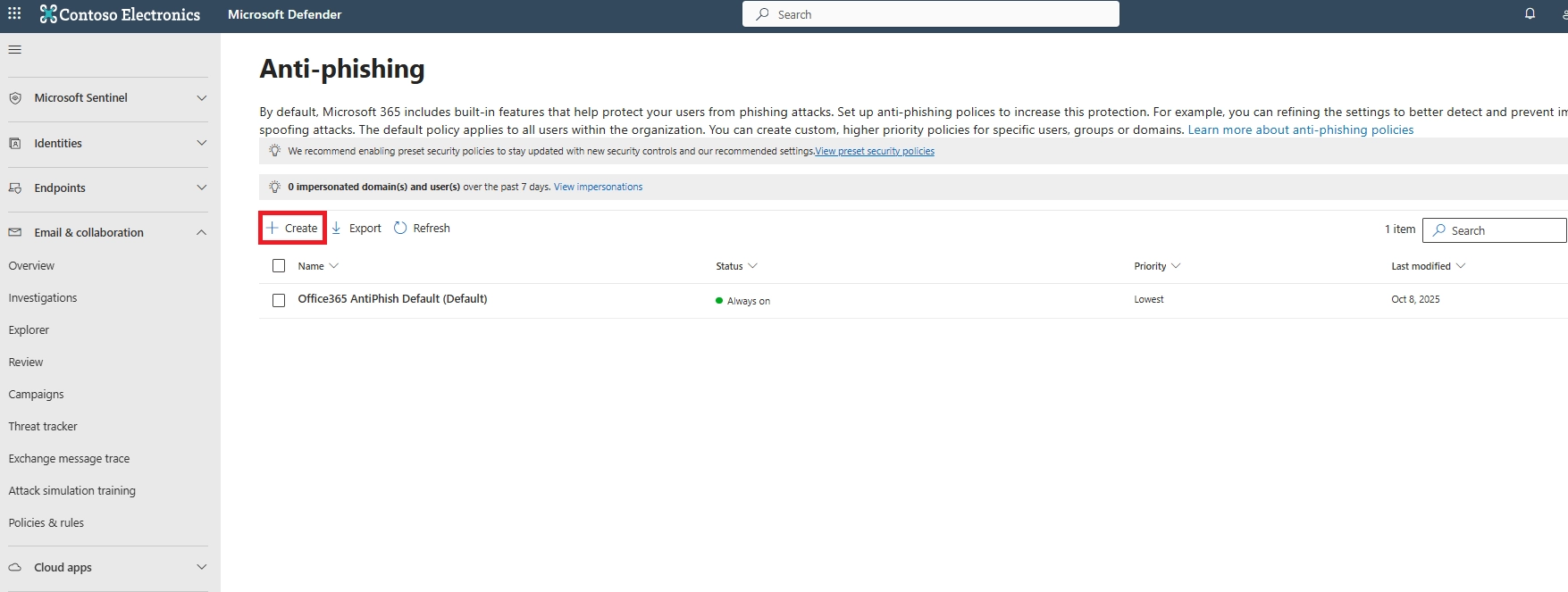
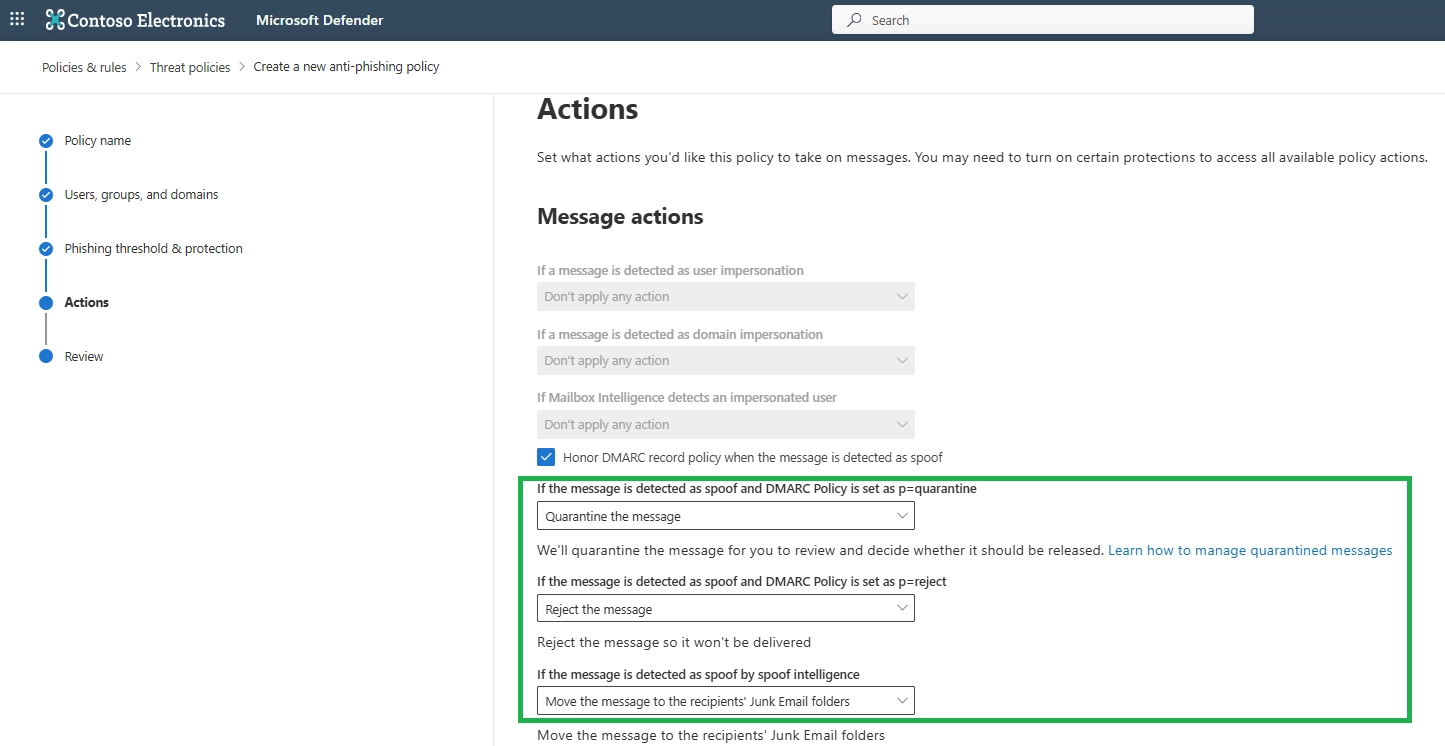
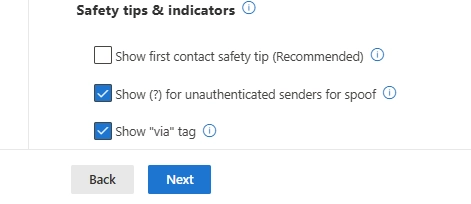
You can set anti-phishing in Microsoft Defender by creating or editing an anti-phishing policy, selecting protected users and domains, and defining actions such as quarantine for detected impersonation attempts.
Q6. How to enable anti-phishing protection in Microsoft 365?
Basic anti-phishing is enabled by default, but advanced protection requires configuring custom anti-phishing policies in Microsoft Defender for Office 365 and enabling impersonation protection settings.
Q7. Which policy helps stop impersonation attacks in Microsoft 365?
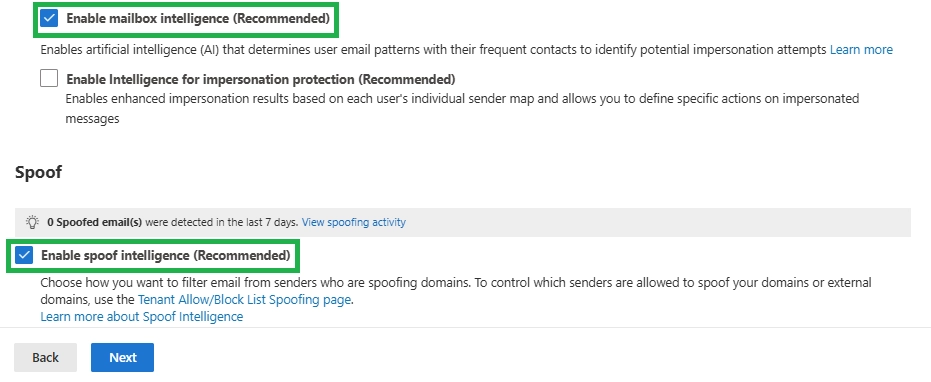
The anti-phishing policy is the main policy used to stop impersonation attacks in Microsoft 365. It works with mailbox intelligence and spoof protection to detect lookalike senders and domains.
Q8. How to check phishing emails in Office 365?
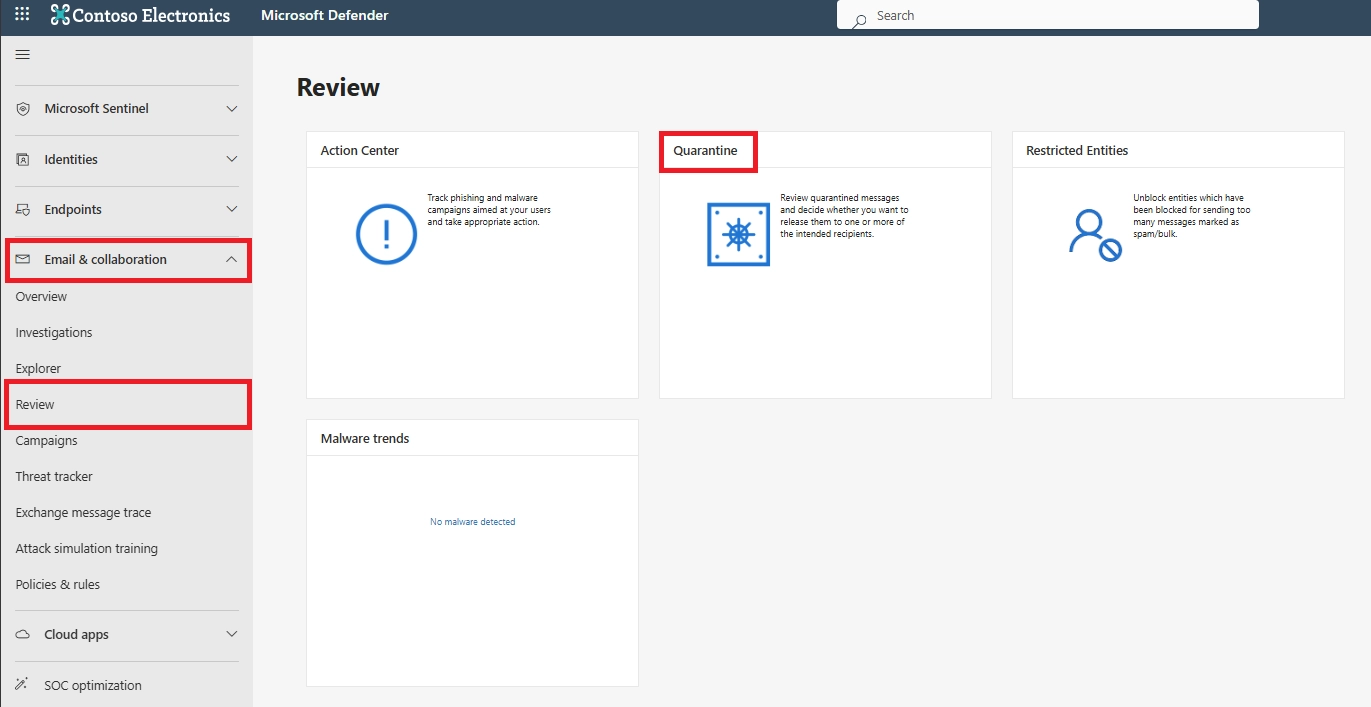
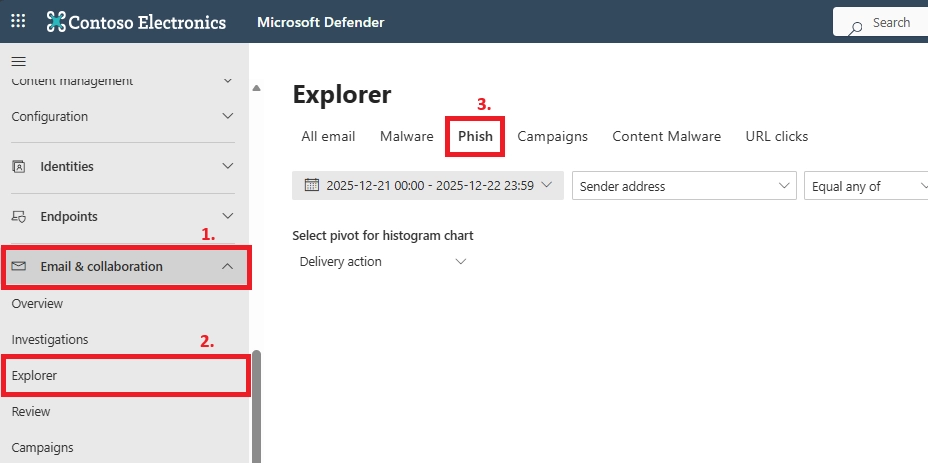
Phishing emails can be reviewed using quarantine, impersonation insights, threat investigation tools, and user-reported phishing submissions inside the security portal.
Q9. What is the difference between antispam and anti-phishing policies?
Antispam policies focus on bulk and unwanted email, while anti-phishing policies specifically protect against impersonation, spoofing, and credential-harvesting attacks.
Q10. What is the phishing policy in Microsoft 365?
The phishing policy defines how Microsoft 365 detects phishing attempts and what action is taken when a message is identified as suspicious or malicious.
Q11. Does Safe Links and Safe Attachments help with phishing protection?
Yes. Safe Links protects against malicious URLs, and Safe Attachments blocks harmful files. Together, they strengthen phishing protection when attackers include links or attachments in impersonation emails.
Q12. Can phishing protection block CEO fraud and vendor impersonation?
Yes. Properly configured impersonation protection can detect and block emails pretending to be executives, finance teams, or trusted vendors.
Q13. What is spoofing protection in Microsoft 365?
Spoofing protection helps stop emails that fake a sender’s domain or identity. It works with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to prevent unauthorized senders from impersonating your organization.
Q14. How do priority accounts improve phishing defense?
Priority accounts receive additional monitoring and visibility, helping admins respond faster when executives or high-risk users are targeted by phishing or impersonation attacks.
Q15. Is user training still needed with Microsoft 365 phishing protection?
Yes. Even with strong technical controls, trained users help identify suspicious emails early and reduce the risk of successful phishing attacks.